Structural Foam Molds
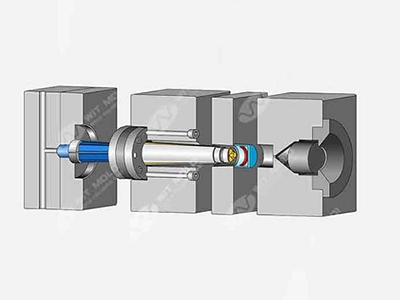
Structural foam molding is a low-pressure foam injection molding process where molten resin is injected with nitrogen gas or a chemical blowing agent. The resin is then shot into the cavity, without overfilling or packing it out. The blowing agent or gas then expands to push the molten resin to the extremities of the cavities. As the part cools, the internal pressure of the foaming action takes up the internal shrinkage and reduces sinks over ribs or heavy cross-sections.
The foam injection molding process can be used on many different sized parts to produce a high strength molded part that is lighter in weight. Many large parts require thicker walls than standard injection molding can effectively produce. Structural foam allows for quicker process and cycle times on thicker parts. This low-cost molding process produces parts that are structurally sound, nearly stress-free and have minimal warpage. The structural molding parts are thicker and sturdier than those created with other processes.